
INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGIES FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT
O.P.IlÆyna[1]
And E.V.Usoltseva[2]
St. Petersburg State University Of Economy And Finance,
Russia
The management of the projects - Project Management (PM) now is the recognized technology of management. It has found a use in various subject domains. The project is understood the term a certain plan, target, sold through the separate interconnected task, with use of resources of a various kind (labor, material and financial, information).
The management of the projects is realized in dynamics. The project begins with the analysis of the current condition and forecasting of development of a problem, search of means and methods of its decision. In result the purposes and tasks of the project are formulated, the necessary degree of quality of the design decisions is determined. Detailed planning of activity both specification of structure and characteristics of use of resources further is carried out. The calendar plan Ś diagram of works is developed, the estimation of time of performance of tasks and project as a whole is given, pay off cost and expenditures of labors of resources, plan of works is accepted. During realization of the project the account and analysis of a course of works is carried out, the administrative cycle is carried out: the analysis existing and forecasting of the future deviations (rejections) from the plan of the project, development of measures on elimination of negative consequences of deviations (rejections), updating of the plan of works etc.
The project is considered as a certain object described by:
the standards of quality and criteria of an estimation of the purposes of the project;
life cycle Ś interval of time from a beginning of development of the project before liquidation of the project;
structure - set of the purposes, interconnected for achievement, of tasks of the project;
structure and volumes of resources, consumed in time, of the certain kind.
Major technical and economic parameters of the project are:
1. Duration of the project.
2. Labor input of works of the project.
3. Cost of realization of the project.
The management of the projects is considered as methodology of organization, planning, management, coordination of labor, financial and material resources during the design cycle directed on effective achievement of its purposes by application of modern methods and information technologies for achievement of certain results on structure and amount of works, cost, time, quality and satisfaction of the participants of the project.
In management of the project it is accepted to allocate:
1. Strategy Ś development of the global purposes of the project, criteria of an estimation of their achievement, creation of the standards of management and standards of quality of management.
2. Tactics Ś detailed calendar scheduling of the project, material maintenance of the project.
3. Operative management and regulation Ś on the basis of the account and analysis of realization of the calendar plans Ś diagrams and actual loading of resources elimination of deviations (rejections) from the base plan of works.
In management of the projects has received development Ņß·ÕĻ“Ē¹ķ the approach, which requires precise allocation of objects administrative influence. Depending on a subject domain such objects are:
industrial objects (production, work or service);
business - processes (business - operation&) including set of operations;
the documents and document circulation etc.
The project assumes interaction of the various participants of process: the users, designers, suppliers, contractors. For the decision of complex problems the advisers are attracted. The investors, owners of the ground areas, financial structures, legal services, bodies of authority can also take part in the project. The general management of the project is carried out by the managers of the project.
The information control systems of the projects should ensure management of the projects during all life cycle. From an information control system of the projects used information technologies of the analysis, planning, forecasting and modeling of the projects the quality and management efficiency depends.
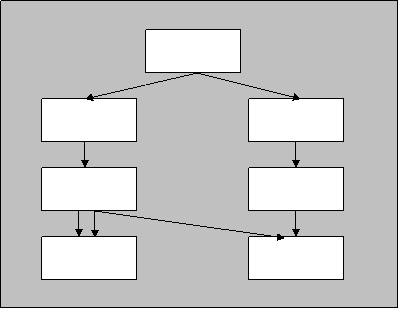
The generalized information and logical model (fig. 1), fixed in a basis of a database of an information control system of the projects, includes information objects:
Calendars (project, task, resource) Ś set of working and non-working days with the instruction of time of functioning of the project, tasks, resources.
The task (work) Ś plan and registration unit of the project, is characterized by a set of properties (identifier of a task, name of a task, type of temporary restrictions, cost, labor input etc.), contains both scheduled, and actual items of information on realization of tasks.


Figure 1
The resource Ś materials, equipment, personnel, industrial areas etc., is characterized by a set of properties (identifier of a resource, kind of a resource accessible quantity, cost etc.), contains both scheduled, and actual items of information on use of resources.
TaskÆs connection Ś parity (ratio) of a beginning and termination (ending) of two connected tasks, contains both scheduled, and actual items of information.
Assignment of a resource Ś quantitative characteristic of interrelation of a resource and task during time of its use (intensity and cost of operation), contains both scheduled, and actual items of information on use of resources in tasks.
For tasks of the project the temporary restrictions influencing a rule(situation) of tasks (in the diagram Gantt, calendar plan - diagram of works) are taken into account. The most typical restrictions on time of realization of tasks are submitted in tab. 1.
Table 1
|
Kind of restriction |
The description |
|
As Soon As Possible (ASAP) - "As soon as possible" |
calculations from a date started of the project |
|
As Late As Possible (ALAP) - " As it is possible later " |
calculations from date of the end of the project |
|
Finish No Later Than (FNLT) - " To finish not later, than " |
the latest date closed of a task |
|
Start No Later Than (SNLT) - " To begin not later, than " |
the latest date started of a task |
|
Finish No Earlier Than (FNET) - " To finish not earlier, than " |
the earliest date closed of a task |
|
Start No Earlier Than (SNET) - " To begin not earlier, than " |
the earliest date started of a task |
|
Must Start On (MSO) - " Should begin in the specified date " |
the exact date started of a task |
|
Must Finish On (MFO) - " Should be finished in the specified date " |
the exact date closed of a task |
For representation of tasks of the project is used network models (columns) ensuring the image of interrelation of tasks of the project in time.
The connection of tasks are set as the certain type of connection and temporary delay (Lag) - tab. 2.
Table 2
|
Type of connection |
An example |
The explanatory |
|
Finish-to-start (FS) Finish - start |
|
The task (B) can not start, the task (A) will not be finished yet |
|
Start-to-start (SS) Start - start |
|
The task (B) can not start, a task (A) yet will not start |
|
Finish-to-finish (FF) The finish - finish |
|
The task (B) can not be finished, while the task (A) will not be finished |
|
Start-to-finish (SF) The start - finish |
|
The task (B) can not be finished, a task (A) yet will not start |
The project has hierarchical structure of tasks, for which image also are used graphic (and sometimes and analytical) means of the description - diagram, table, matrix of a contiguity etc.
In a fig. 2 the types of tasks of the project are represented:
Ę simple (further indivisible) task - as circles;
Ę compound (total) tasks - as rectangular;
Ę milestone (control points) - as triangles;
Ę periodic tasks - as a rhombus.
The structure of entry of tasks is described by a structural code - Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). On the basis of a structural code of tasks of the project the cost and temporary characteristics of a various level aggregation are calculated.
At a choice of software for information control systems of the projects it is necessary, first of all, to estimate specificity of the project, having analyzed character of activity of organization from the point of view of an opportunity and expediency of application of the design form of planning and management. Thus it is necessary clearly to represent, what activity can be planned as the projects, as far as it is in details necessary plan and supervise the projects.
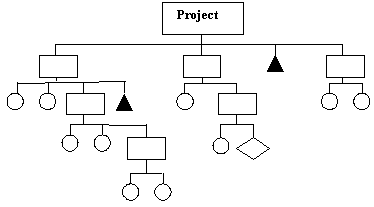
Figure 2
The basic distinctions of software of information control systems of the projects:
¦ cost of the software;
¦ functions of management of the projects;
¦ dimensions of the characteristic of the developed projects (" capacity " of the projects);
¦ opportunities of information integration of the project with external information systems;
¦ the requirements by operational environment(Wednesday) and means etc.
At an estimation of software of information control systems of the projects it is necessary to pay attention to quality of the user interface Ś structure and assignment of instructions of the menu, panel of tools, external representation of tasks and resources of the project, support paradigm of management (analysis, plan, control etc.). For specification of the calendar plans Ś diagrams the software should supply conducting various calendars (project, tasks, resources). The tasks of the project should easily be structured.
The quantitative restrictions of the project (maximal duration of the project, limiting number of tasks of the project, maximal depth of an enclosure of tasks allowable kinds of connections of tasks, maximal number of resources etc.) for various software of management of the projects of one price level are approximately identical. Therefore greater attention should be given the analysis of structure Data Base (DB), describing properties of tasks and resources, and also opportunities of its expansion.
In software of an information control system of the projects the following kinds of data processing of the project should be submitted:
¦ the sample description of the project (method " of the prototypes " for the new projects);
¦ multidimensional representation of the information about the project (screen forms, diagrams, reports);
¦ sorting, search and filtration given of the project by various criteria (query language of a high level);
¦ creation of the global projects by association of the projects and allocation subprojects;
¦ the temporary and cost analysis of the project;
¦ balancing of loading of resources of the project;
¦ means of the account and control of a course of works of the project;
¦ the forecast of meanings of temporary and cost parameters of the project;
¦ documenting of the project at various stages of his(its) preparation and use, including in a network the INTERNET / intranet;
¦ joint work in a network of the members of a team of management of the projects;
¦ automation of performance of routine actions (macros, program modules) etc.
The most widespread software for creation of control systems of the projects are:
Microsoft Project (firm Microsoft) Ś is focused on the modern standards of information technologies, supports group work with the projects in global and local networks (Microsoft Mail and Microsoft Exchange). Has convenient means of creation of the reports, modeling of the projects - analysis " that if ", but the means of planning and resource management are not powerful enough for the complex projects.
Time Line (firm Time Line Solutions) Ś realization of the multiprojects within the framework of organization, flexible means of formation of the user information convenient algorithms of alignment of loading of resources for the multiprojects. Well approaches for creation of the projects of average complexity and cost.
Primavera Project Planner - P3 (firm Primavera Systems, Inc.) Ś powerful system of planning and management of the large-scale projects on the basis of modern network technologies. Provides a necessary level of a grouping of tasks and resources of the project, multidimensional description and special resource planning, the analysis is brave, formation of the accounting documentation.
Spider Project (firm Spider Technologies Group) Ś domestic development focused on flexible purpose(assignment) of resources to tasks of the project, alternative designing, optimization of the design decisions in a part of assignment of resources, information support of various technologies of subject domains (use of the specifications of productivity of resources and cost of works etc.).
Introduction information system of project management expects performing the complex of the works:
¦ Installation and mastering of software of project management.
Preparing the command of the projectÆs managers.
Creation projectÆs templates.
The categorization and standardization resources.
Creation database for projects.
Testing system of project management.
The difficulty of the introduction of information technology for project management depends of next factors:
the scale and structures of system organization;
the existing level of automations;
projectÆs and resourceÆs specifics;
participations of external organizations in project management and others.
It is recommended begin with planning and checking project's temporary parameters. Here on execute resource's planning, including balancing the loading resources. Then master the functions cost analysis, planning, checking and forecasting of the projectÆs parameters.
Introduction system of project management must occur consecutively, as from small and uncomplicated project, for which obvious positive results of the using information technology. Here in after possible introduce the more complex projects, create the resource's pools (the association of interchangeable resource), go to multi-project management.